- Gas chromatographs
- Gas generators
- Software
- Sample injection devices
- Service devices
- MEASURING EQUIPMENT
-
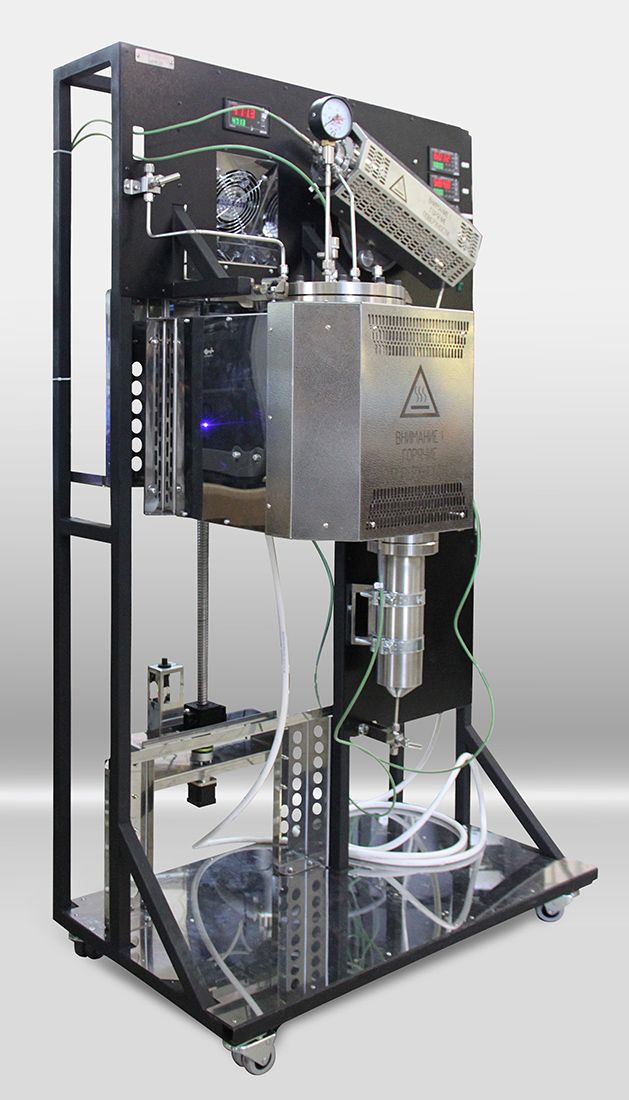
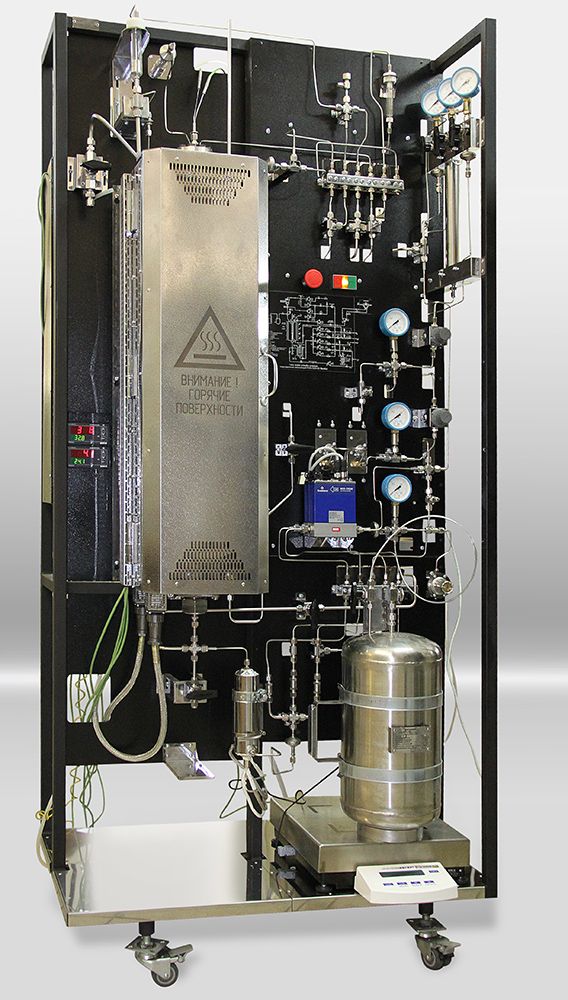
Laboratory reactor unit
- Automatic attrition tester
- Pirolysis instrument
- The laboratory unit
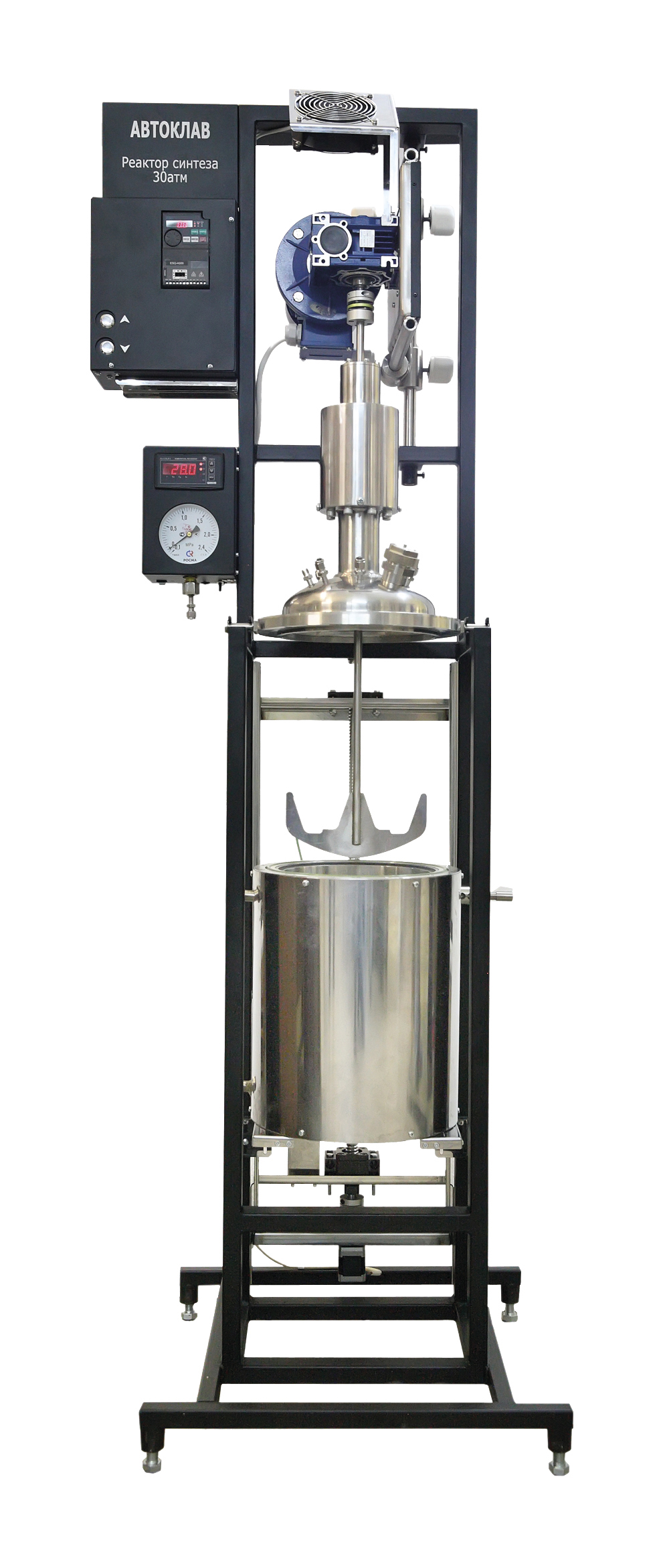
- Autoclave laboratory reactor
- Pilot coking unit
- Hydrotreating-reforming unit
- Bench laboratory reactor
- Automated laboratory testing unit for isobutane dehydrogenation catalyst (kdi, kdi-m) in fluidizen bed layer
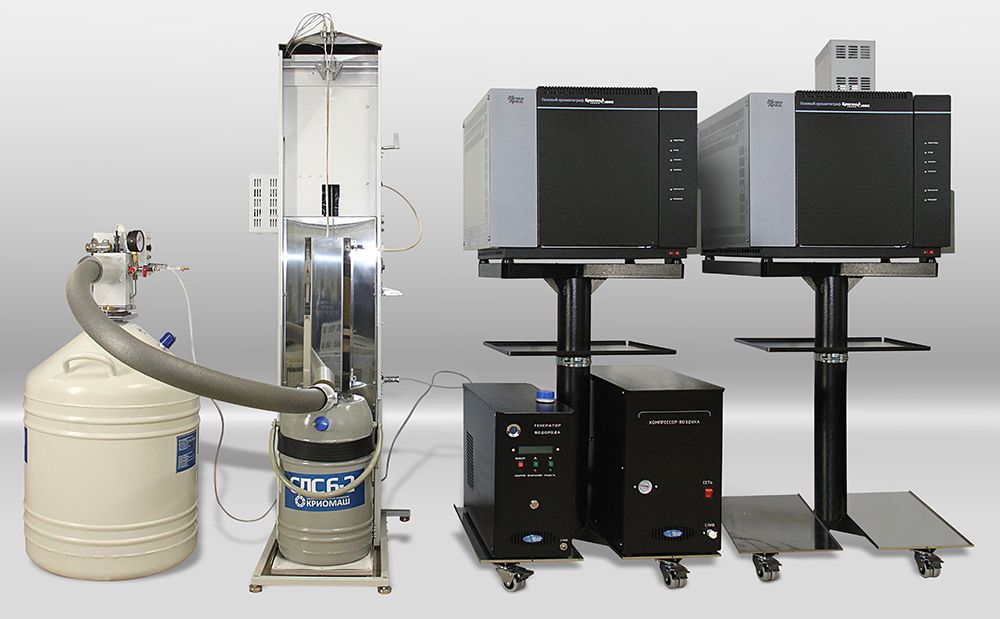
- Cryoconcentration unit CCU-6
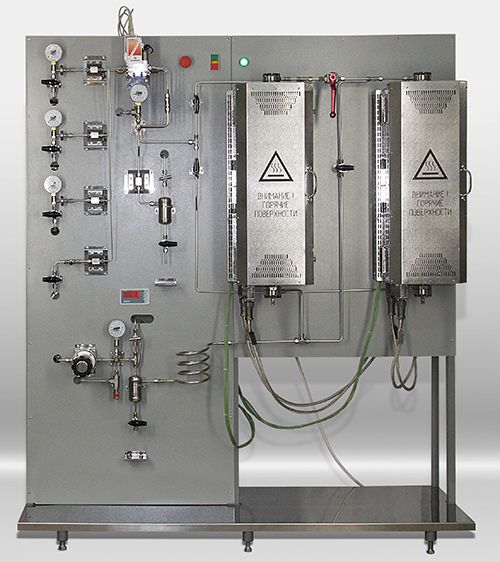
- Two-channel laboratory unit for evaluating
- Pipe thermostat
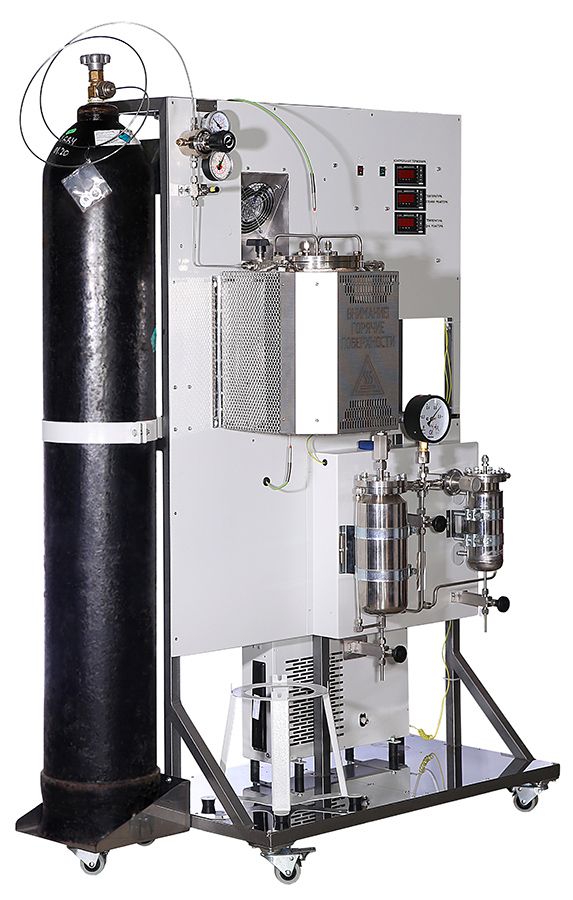
- Laboratory of catalytic unit for petrochemical industry
- Universal bench laboratory unit
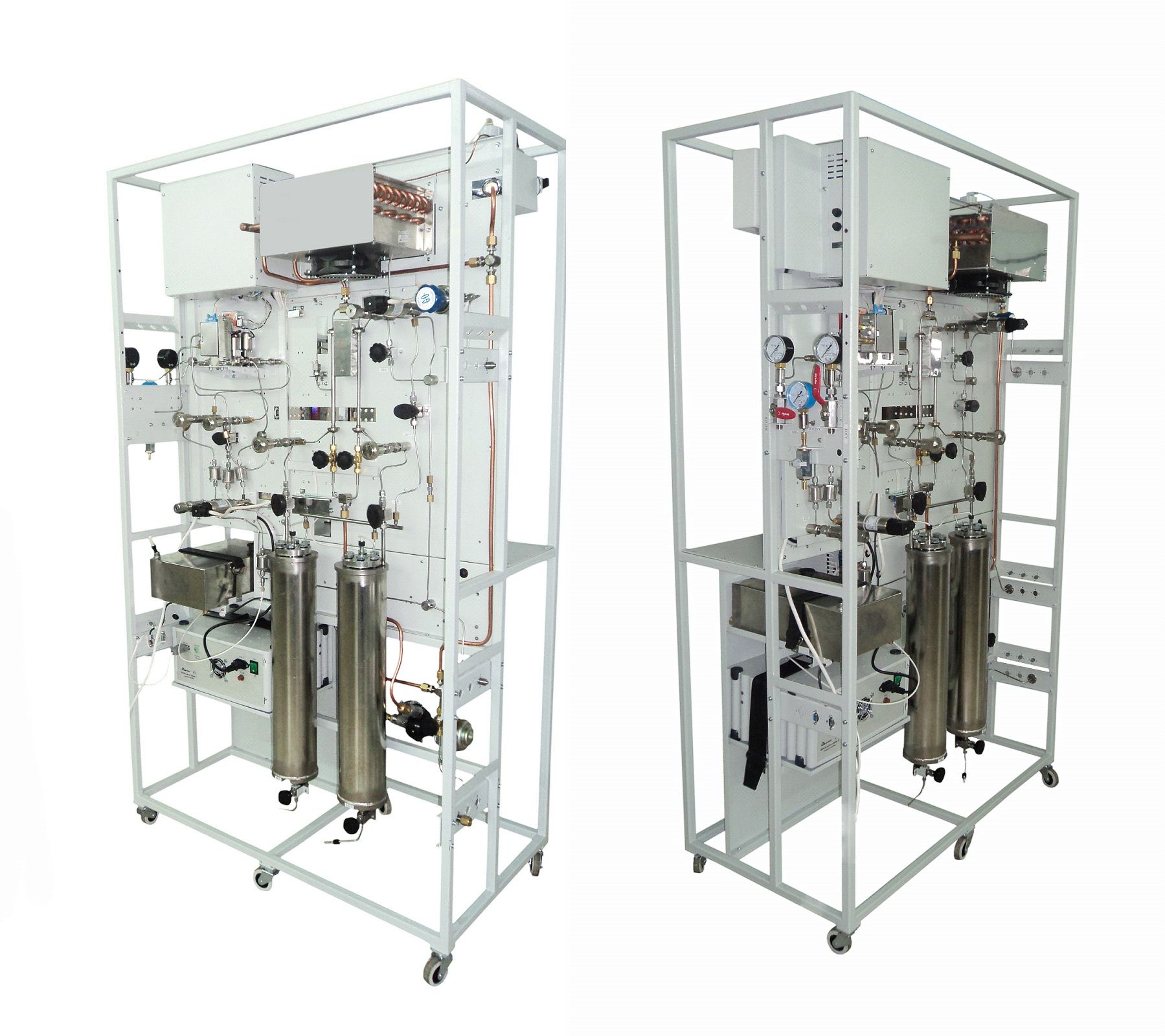
- Reactor unit design
- Unit of propylene steaming
- Pyrolyzer
- Device for testing friction and abrasion of catalysts "PTI-1"
- Automatic attrition tester by air jet for fluidized bed cracking catalysts by express-method
- Laboratory catalytic unit lcu-1
- High-temperature furnaces
- Pilot unit for catalytic propylene oxidation reactions
- Reactor unit for testing catalysts for hydrodewaxing and isodewaxing of base and other oils.
- Unit for petroleum pitch obtaining
- Pilot unit for delayed coking
- Unit for testing activity and selectivity of fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts in fluidized bed according to ASTM D7964/D7964M-19
- The laboratory catalytic dewaxing unit
- Hydrogen station
- Bench laboratory unit for studying gas chemical processes and implementing GTL technologies according to Fischer-Tropsch.
- Automatic six-channel unit for carbon monoxide index determination
- Single-channel hydrotreating unit with up to 20 MPa working pressure
- Automation of old chromatographs
Operating modes of the unit:
1. Gas monophase (the phase state of the reagents at room temperature - liquid or gas).
2. Liquid monophase (phase state of reagents at room temperature-liquid).
3. Two-phase (heterophase system gas – liquid).
4. Temperature: working range 500ºC-6000ºC, 8000ºC (three-zone heating furnace).
5. Pressure: operating range 0,1-60, 100, 200 MPA
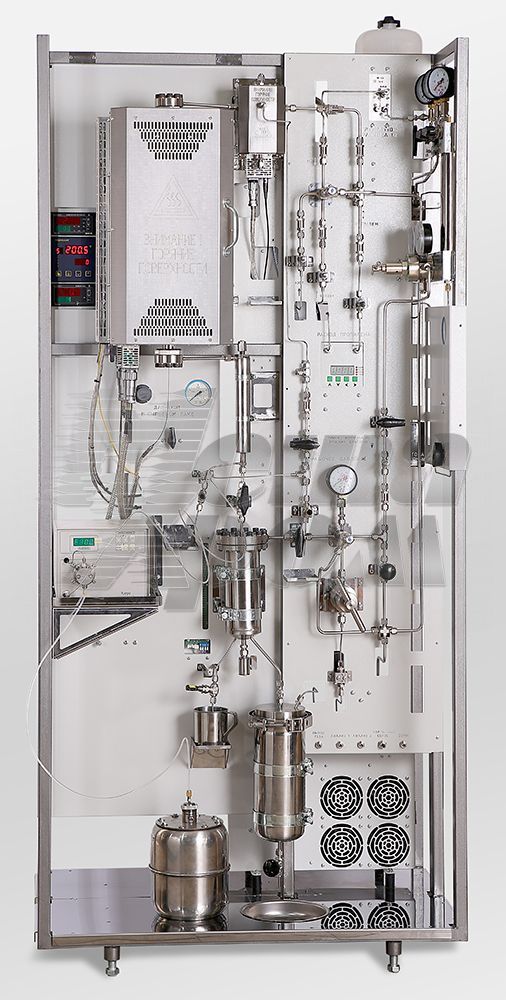
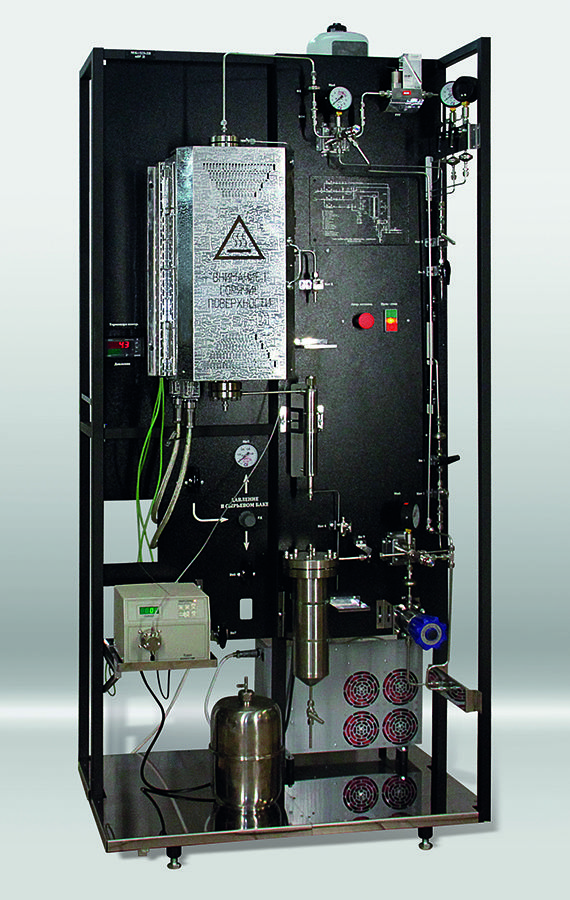
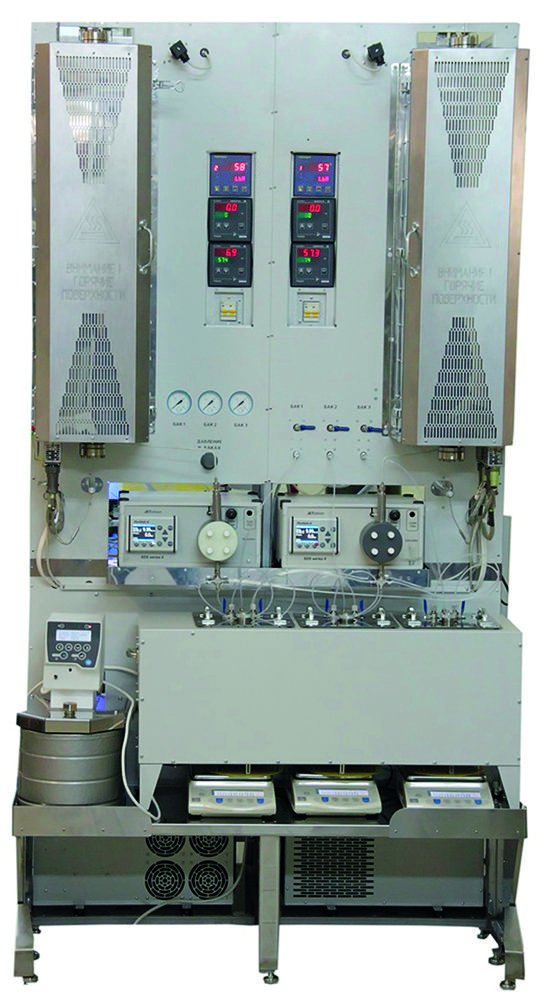
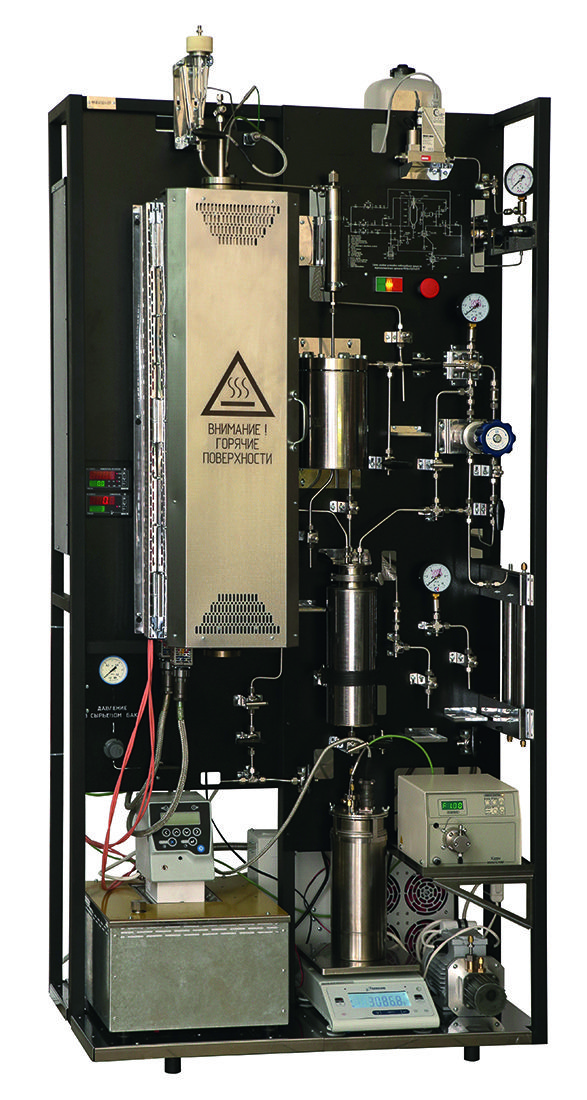
In the photo: Universal bench laboratory unit for the study of the processes of basic organic synthesis in a reactor with a fixed catalyst bed
The unit is designed (tested) for the study of a wide range of heterogeneous catalytic reactions, including:
1. Hydrogenation processes in the gas phase.
2. Hydrogenation processes in the liquid phase.
3. Gas-phase dehydration of aliphatic and aromatic alcohols.
4. Dehydration of aromatic alcohols in the liquid phase.
5. Alkylation of aromatic hydrocarbons by olefins and alcohols.
6. Hydroalkylation of aromatic compounds by ketones.
7. Dehydrogenation of chemical compounds of different classes.